
The solenoid was internally leaking a small amount of oil, just enough to soak the electrical connector.Įlectrical contact cleaner and a new OCV solenoid repaired the vehicle. We recently had a late-model V6 minivan in our lab with one of these codes. OCV solenoid circuit faults include P0010 and P0013. Regardless of control specifics, the PCM monitors solenoid circuits for faults including opens, shorts to ground or shorts to voltage. OCV solenoids are typically cycled upon ignition run mode as part of a cleaning and diagnostic strategy. I found versions of both on our laboratory vehicles. They ranged between 7 and 12 ohms of resistance.īoth circuits connect to the PCM, which provides duty-cycle control either on ground or the insulated (power) side. I measured the resistance of several solenoids from various manufacturers. It should be noted that service information does not recommend phaser disassembly and individual parts are unavailable.Īs for service parts, phasers are sold as an assembly.Įlectrically, the OCV solenoid has two terminals. In the default position, there is no valve overlap.
#DODGE VARIABLE VALVE TIMING FULL#
The locked phaser positions on this engine are full retard on the intake and full advance on the exhaust.īecause of the clockwise rotation when viewed from the front of the engine, the exhaust rotor requires additional assistance in reaching the full advance position.
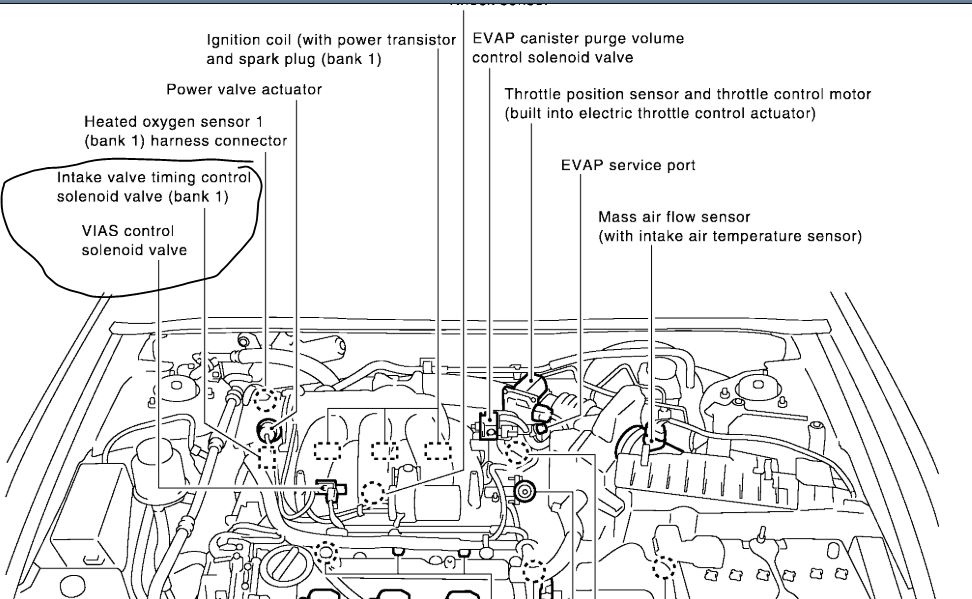
The 2.4L Chrysler engine that I disassembled also featured a spring on the exhaust camshaft. Oil pressure is required to disengage the lock pin. The lock pin prevents noise and potential wear upon engine start. The spring-loaded lock pin on the rotor engages into the phaser body to lock the two pieces together. There is a mechanical device inside the phaser known as a lock pin. Vented oil from the phaser ports travels back through the camshaft, the cam bearing ports, through the oil control valve and then drains into the front timing cover.
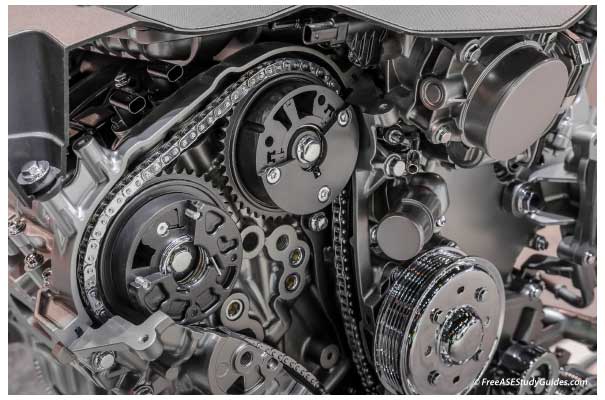
Oil seals fit into machined grooves of the rotor to provide a tight seal between the chambers. Ports inside the phaser direct oil in or out of eight chambers.įour chambers are considered side “A” and the other four are side “B.”Īs one group of chambers receives pressurized oil, the others are vented to provide the force necessary to move or hold the rotor relative to the phaser body. The two pieces are able to move about 20° (40 crankshaft degrees) independently of each other. The rotor is connected to the camshaft using a dowel pin. The phaser body is physically bolted to the camshaft sprocket. The phaser is a mechanism with two major pieces, the rotor and the phaser body. Oil flows though passageways inside and toward the front of the camshaft.Īt the nose of the camshaft, oil enters ports of the camshaft phaser. Pressurized oil travels through the OCV to one of the camshaft bearing journals. It determines which ports receive pressurized oil and which are vented. The OCV is an oil traffic control device of sorts. The PCM (powertrain control module) duty-cycles a solenoid that alters valve position. The OCV is a spool valve much like those found in automatic transmissions. The major control component in camshaft phasing is the oil control valve (OCV). Sensors that monitor oil pressure and oil temperature are common on VVT engines and are a part of system control strategy. Replacing these screens often requires major engine disassembly.

Oil pressure is critical, and as bearings wear and develop clearance, pressure will be affected.Įngines are machined with additional oil galleys for VVT and are equipped with one or more fine mesh screens to prevent debris from entering components. Low oil level or the wrong viscosity can result in system slow response codes such as P000A or P000B and possible drive complaints including an illuminated MIL. That means it is imperative that engines are filled to the correct level with clean motor oil of the proper viscosity. Motor oil is the hydraulic medium that makes VVT work. Mechanical, hydraulic and electrical controls have been added to VVT engines. If you are not familiar with these units, it’s time to advance your diagnostic readiness by examining the VVT system, its controls and operation. VVT presents additional diagnostic challenges and repair opportunities to the service industry including new trouble codes. This gives engineers flexibility in improving fuel economy and power while continuing to meet emissions standards. Phasers commonly can be found on just the exhaust cam or on both the intake and exhaust cams.Īlteration of camshaft position changes the cam centerline and the lobe separation angle between intake and exhaust cams. In this hold position, neither chamber receives pressure nor is drained. Figure 2: The oil control valve is the traffic control device of oil pressure.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
